Parts of the liver
The liver lobes, they are part of the parts of the liver and are ligaments that are divided into left and right.
Although there are other types of lobes that are considered sub-parts of the left hepatic lobe called caudate lobe and square lobe.
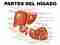
Another part is the gallbladder, which is on the back of the liver and is sac-shaped; Then there is the common bile duct which is also known as "common bile duct", it is through it that the bile substance travels towards the gall bladder and then it is conducted to the duodenum for the digestion process.
Fatty liver, as its name implies, is a condition where fat accumulates in the organ. This occurs due to a failure in the proper functioning of the liver. In the human body we can find many...webmediums.com
The liver is also made up of other ligaments called triangular ligaments. which are formed by the coronary ligament that is responsible for the union between the back of the diaphragmatic area of the stomach with the diaphragm as such - then there is the round ligament, is directly connected to the umbilical cord, has a fibrous texture and goes from the back of the navel to the underside of the liver.
And finally there is the falciform ligament, which is responsible for connecting the stomach with the diaphragm and the part that goes to the abdominal wall.
The liver has the responsibility of supplying various functions at the metabolic level in the body, which is why Chinese medicine considers it one of the organs that demands the most attention. ...webmediums.com
The last two parts of the liver are the arteries, this is the hepatic artery that come from the celiac trunk, these go along the liver being a horizontal that goes to the gastro-duodenal and an ascending that goes directly to the hilum of the liver.
The portal artery, which is responsible for the transport of blood and all the nutrients and vitamins necessary for the proper functioning of the liver. For being right is the thickest and thus can facilitate metabolism. Its walls are thin, and at its maximum development reaches a thickness of up to 20 millimeters.
